服务价格:
服务分类:
所用仪器:
依据标准号:
依据标准号:

Creative Proteomics offers iTRAQ protein quantification service suited for unbiased untargeted biomarker discovery. Relative quantification of proteins for biomarker discovery in complex mixtures by mass spectrometry can easily and quickly be achieved using iTRAQ technology. iTRAQ is ideally suited for comparing normal, diseased, and drug-treated samples, time course studies, biological replicates and provides relative quantitation.
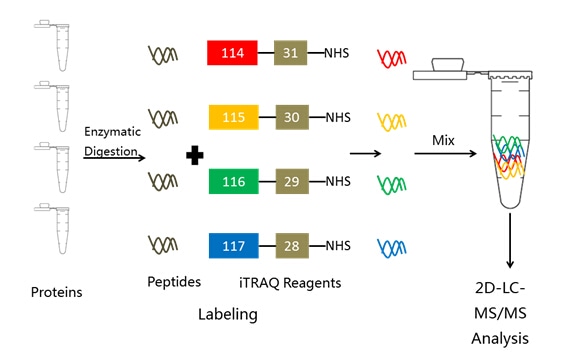
Protein quantification through incorporation of stable isotopes has become a central technology in modern proteomics research. Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ) is used in proteomics to study quantitative changes in the proteome.
iTRAQ-based quantification facilitates the comparative analysis of peptide and proteins in a variety of settings including comparison of normal, disease or drug treated states.
The iTRAQ technology utilizes isobaric reagents to label the primary amines of peptides and proteins. The iTRAQ reagents usually consist of an N-methyl piperazine reporter group, a balance group, and an N-hydroxy succinimide ester group that is reactive with the primary amines of peptides. The balance groups present in each of the iTRAQ reagents function to make the labeled peptides from each sample isobaric and the quantification is facilitated through analysis of reporter groups that are generated upon fragmentation in the mass spectrometer. There are currently two mainly used reagents: 4-plex and 8-plex, which can be used to label all peptides from different samples/treatments. These samples are then pooled and usually fractionated by nano liquid chromatography and analyzed by tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS).
http://www.creative-proteomics.com/services/itraq-based-proteomics-analysis.htm
| 合同甲方 | 送样单号 | 合同编号 | 评价 | 评语 | 评价日期 |
免费发布咨询信息!
与实验室管理人员面对面沟通。